Ever wake up scared from dreams of drowning or trouble breathing? If you have sleep apnea, these nightmares might be connected. Sleep apnea stops you from breathing while you sleep, lowering blood oxygen. This makes your brain feel stressed.
Studies show 43.2% of sleep apnea patients remember their dreams. This is less than those without it, who remember 71.4% of their dreams. But why is there such a big difference?
A 2019 study found people with sleep-breathing issues have more unusual dreams. The brain reacts to oxygen drops during apnea events. This can lead to vivid, scary dreams.
Nightmares about suffocation reflect the real physical strain. This creates a haunting cycle. Anxiety from not getting enough sleep makes things worse. 10% of the world’s population faces OSA and its effects.
Key Takeaways
- 43.2% of sleep apnea patients remember dreams, vs. 71.4% without the condition
- Oxygen loss during apnea episodes may trigger fear-based nightmares
- CPAP therapy improves REM sleep, reducing nightmare frequency
- Anxiety linked to sleep apnea increases bad dream likelihood
- Children and adults with OSA often report suffocation-themed dreams
Understanding Sleep Apnea and Its Common Symptoms
Millions of Americans have sleep apnea. This is when breathing stops and starts while sleeping. These pauses can lead to sleep apnea symptoms nightmares. Knowing the basics helps spot risks early.
What Exactly Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea comes in three types, with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) being the most common. In OSA, the throat muscles relax, blocking air. This can harm your heart and brain without treatment.
Many with severe OSA have fewer dreams but vivid nightmares. These nightmares often involve suffocation or drowning.
Different Types of Sleep Apnea
| Type | Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) | Physical airway blockage | Snoring, gasping, morning headaches |
| Central Sleep Apnea | Brain fails to signal breathing muscles | Shortness of breath, insomnia, fatigue |
| Complex Sleep Apnea | Mix of OSA and central apnea | Combination of both types’ symptoms |
Recognizing the Warning Signs
- Loud snoring followed by silent pauses
- Gasping/choking sounds while sleeping
- Daytime fatigue even after “enough” sleep
These signs are linked to connection between sleep apnea and nightmares. Anxiety from poor sleep can make dreams more intense. This can harm your mental health over time.
Acting early is key. If you notice these signs, keep a sleep journal. Losing weight or sleeping on your side might help. But if nightmares don’t go away, see a specialist.
The Nature of Nightmares and Their Impact on Sleep Quality
Nightmares are scary dreams that wake you up. They happen during REM sleep, when dreams are most vivid. While most people have nightmares sometimes, too many can mean a bigger problem.
Studies show 5% of adults have nightmares often. Up to 75% of PTSD patients have nightmares too. Nightmares are different from night terrors because you remember them.
They can wake you up in the middle of the night. This makes it hard to sleep well. People who have nightmares often wake up feeling tired and groggy.

Medicines and withdrawal can cause nightmares. Sleep apnea can make nightmares worse by interrupting sleep. Waking up to breathe can make dreams more intense.
Identifying what causes nightmares is the first step. If you snore a lot or wake up gasping, sleep apnea might be the reason. Untreated sleep problems can make nightmares and health issues worse.
A sleep study can find the cause. It can help you feel better with treatments like special devices or therapy.
Does Sleep Apnea Cause Nightmares? Examining the Evidence
Research shows a complex link between sleep apnea and nightmares. Some studies find a sleep apnea nightmares correlation. But others show different patterns. Let’s look at what science says and what patients feel.

Scientific Research on the Connection
A big study followed 393 patients. It found a surprising fact: those with severe sleep apnea reported fewer nightmares. Here are some examples:
- Patients with AHI over 30 had 20.6% reporting frequent nightmares.
- Those with mild apnea (AHI under 5) had 71.4% frequent nightmares.
- Higher oxygen levels during sleep were linked to more nightmares.
How Oxygen Deprivation Affects Dream States
Oxygen drops during apnea events can mess with REM sleep. This is when dreams are most vivid. Low oxygen might suppress nightmare recall. But it can also lead to intense dreams filled with anxiety.
Many patients dream about drowning or suffocation. These dreams mirror their struggle to breathe at night.
Patient Experiences and Case Studies
“After starting CPAP therapy, my nightmares about choking vanished completely.”
Real-life stories match the data: 91% of CPAP users saw their nightmares go away. But those not using treatment often have worse dreams. Case studies also show:
- Severe OSA patients with low nightmare recall had average AHI scores 2x higher than those with frequent nightmares.
- Women reported more detailed dream narratives but less nightmare frequency compared to men.
- CPAP use cut nightmare frequency by 50% in PTSD patients with OSA.
Science may debate the exact link, but your own experience is key. If you notice scary dreams tied to breathing issues, talk to your doctor. It could be a sign of your sleep health.
How Sleep Apnea Disrupts Normal Sleep Cycles
Understanding sleep apnea and nightmares starts with sleep stages. Sleep apnea stops the natural flow of REM sleep. REM is when you dream vividly, including nightmares.
When you stop breathing, your body gets stressed. This can change your dreams or make you forget them.
REM Sleep Disturbances and Dream Intensity
REM sleep starts 90 minutes after you fall asleep. It’s when your brain deals with emotions and memories. Sleep apnea can make your dreams more intense or make you forget them.
This depends on how broken your sleep is. So, does sleep apnea cause nightmares depends on your sleep quality.
- REM suppression: Apnea can shorten or skip REM, making you remember fewer dreams.
- REM rebound: After treatment, some dream more because their brain is catching up on REM.

The Role of Sleep Fragmentation in Nightmare Development
| Normal Sleep | Apnea-Affected Sleep |
|---|---|
| Uninterrupted REM phases allow natural dream processing. | Gasps/wake-ups break REM, leading to fragmented, intense dream fragments. |
| Memory consolidation happens smoothly during deep sleep stages. | Repeated awakenings disrupt memory sorting, possibly increasing nightmare frequency. |
Fragmented sleep also makes your brain work harder to handle stress. This can make anxiety dreams worse. For example, 50% of OSA patients have suffocation dreams linked to their breathing issues.
Your sleep cycle is very important. Fixing sleep apnea with CPAP or lifestyle changes can help. This can reduce nightmares and improve your sleep.
Other Sleep Disorders That May Trigger Nightmares
While the connection between sleep apnea and nightmares is clear, other sleep disorders can also cause bad dreams. Knowing these connections helps find the main cause of your nightmares. For example, nightmares linked to sleep apnea often involve feelings of being suffocated. This is because of airway blockages during REM sleep.

- REM Behavior Disorder: Causes acting out vivid dreams, sometimes mistaken for sleep apnea-related panic.
- Narcolepsy: Daytime sleepiness and sudden muscle weakness can blur the line between sleep disorders.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): Twitching legs at night may disrupt sleep, amplifying anxiety-driven dreams.
Children often have night terrors—sudden screams or fear without recall. Adults with sleep apnea might dream of suffocation. Note that sleep apnea symptoms nightmares differ: adults with apnea remember fewer dreams overall (only 43.2% recall them vs. 71.4% in healthy sleepers).
Mental health also plays a role. PTSD, anxiety, or depression can make nightmares worse. Medications like beta-blockers or antidepressants might also cause bad dreams. If nightmares keep happening, track your sleep and talk to your doctor. Recognizing these links helps tailor treatments like CPAP therapy or counseling for better rest.
Diagnosing the Connection Between Your Sleep Apnea and Nightmares

If you think sleep apnea causes nightmares, there are steps to find out. Keeping track of symptoms and sleep can show how breathing issues might lead to bad dreams. We’ll look at how to figure out the impact of sleep apnea on nightmares through doctor visits and tools for tracking sleep.
When to Talk to Your Doctor
See a specialist if you notice:
- Frequent gasping awakeningsgs paired with fearful dream content
- Daytime exhaustion despite 7+ hours of sleep
- Patterns where nightmares align with choking sensations during rest
Sleep Studies and Their Importance
Tests like polysomnography show how sleep apnea and nightmares are linked. Here’s how it works:
| Test Type | In-Lab Polysomnography | At-Home Study |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Tracks brain waves, oxygen levels, and breathing | Measures oxygen and breathing patterns |
| Setting | Overnight clinic stay | Conducted in your own bed |
| Use Case | Best for detailed sleep architecture analysis | Convenient for initial screening |
These tests show if oxygen drops during apnea episodes match nightmare times. This helps understand the sleep apnea nightmares correlation.
Keeping a Sleep and Dream Journal
Use this guide to record your nights:
- Note dates and nightmare content (e.g., suffocation themes)
- Record breathing interruptions or snoring episodes
- Track daytime mood changes like anxiety or fatigue
Studies show only 43.2% of sleep apnea patients remember dreams, compared to 71.4% of healthy sleepers. Keeping a journal helps doctors see how sleep problems affect dreams. Regularly logging your experiences can show important patterns that help understand the impact of sleep apnea on nightmares.
Treatment Options That Address Both Sleep Apnea and Nightmares
If you want to stop nightmares caused by sleep apnea, start by treating the sleep apnea. This can help reduce nightmares and improve sleep. First, see a doctor to find the best treatment for you.

- CPAP Therapy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure devices keep airways open, restoring normal breathing. Studies show CPAP improves REM sleep, which may cut nightmare frequency over time.
- Oral Appliances: Custom mouthpieces reposition the jaw, ideal for mild cases. They’re a discreet alternative to CPAP machines.
- Positional Therapy: Sleeping on your side prevents airway blockages and reduces disruptions during deep sleep phases.
To fight nightmares, add lifestyle changes to your treatment. Avoid alcohol before bed and practice relaxation techniques. Also, keep a regular sleep schedule. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT-I) can help change negative sleep patterns.
Treating sleep apnea can also help control dreams. Over 70% of patients say they have fewer nightmares with regular CPAP use. Don’t wait—early treatment can help you sleep better and feel better overall.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Sleep Quality and Reduce Nightmares
Small changes in your daily life can help a lot. A calm place, eating mindfully, and managing stress can ease symptoms. Let’s look at simple steps to better your sleep.
“Sleep apnea can lead to an increase in nightmares due to oxygen deprivation and fragmented sleep.”
Creating an Optimal Sleep Environment
First, make your bedroom the best place to sleep. Keep it cool (65–68°F) and dark. This helps you breathe better and reduces blockages.
Use a humidifier to stop your nose from getting stuffy. Also, place your bed so your head is slightly higher. Avoid screens for 1–2 hours before bed to stop blue light from messing with your sleep.

Dietary and Exercise Considerations
Don’t drink caffeine or alcohol in the evening. They make apnea worse and cause vivid dreams. Eat dinner 2–3 hours before bed to avoid acid reflux.
Try to exercise for 30 minutes each day (like walking or yoga). This helps with apnea and sleep. But, don’t work out too close to bedtime.
Stress Management Techniques
Try deep breathing or meditation before bed. This lowers stress and apnea episodes. Writing down your dreams and stressors each night can help spot patterns.
Try progressive muscle relaxation. Tense and then relax each muscle group from your toes to your head. This calms your body for sleep.
These steps are a good start for better sleep. Add them to medical treatment for the best results. Small, steady efforts can cut down on sleep apnea linked to nightmares and boost your overall health.
Using CPAP Therapy to Reduce Nightmare Frequency
CPAP therapy is a proven sleep apnea treatment for nightmares for many. It helps keep breathing steady during sleep. This leads to better REM cycles, reducing stress that can cause nightmares.
A 2013 VA study found veterans with PTSD and OSA saw nightmare frequency drop when using CPAP consistently.
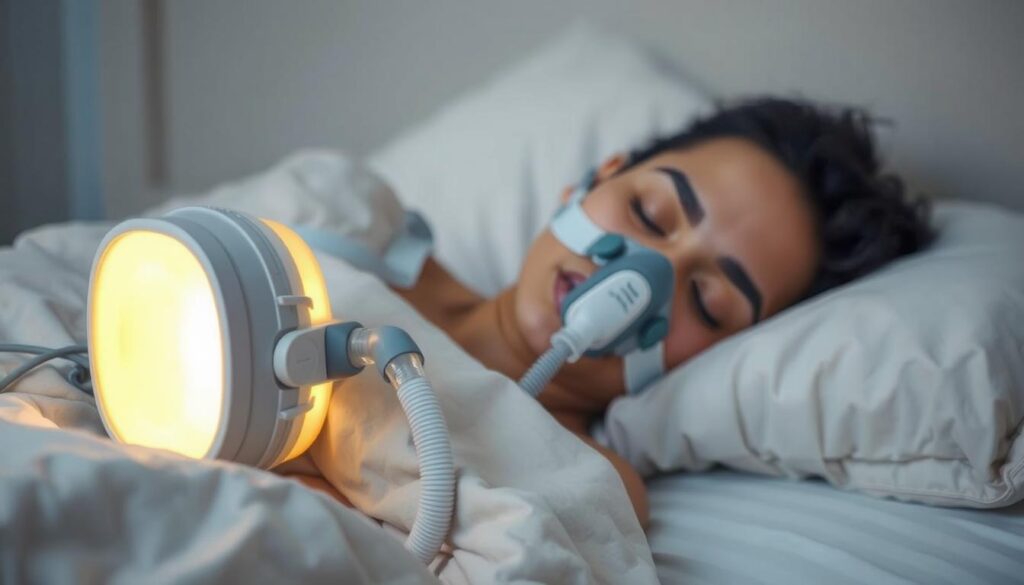

A 2013 VA study showed 60% of participants using CPAP saw fewer nightmares after 3 months of regular use.
Here’s how to maximize results:
- Ensure your mask fits snugly to prevent air leaks.
- Adjust humidity settings to avoid dryness or irritation.
- Use the ramp feature to ease into pressure levels gradually.
- Track usage with a CPAP device’s built-in data features.
When sleep apnea and nightmares persist, talk to your doctor. Mask leaks or incorrect pressure settings can still cause oxygen dips, triggering distressing dreams. Consistent use of your machine is key—studies show 90% compliance reduces nightmare frequency by 50% or more. If symptoms linger, a sleep specialist can re-evaluate your therapy settings.
Remember, better oxygen flow during sleep helps your brain process emotions differently. Over time, nightmares may fade as your body adapts to stable breathing. Prioritize nightly use and communicate openly with your care team to optimize this life-changing therapy.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Sleep Health
Ever wondered if sleep apnea causes nightmares? The answer is yes, for some people. Not everyone with apnea has scary dreams. But, severe cases often lead to more disturbing dreams.
Treating breathing problems like sleep apnea can help. It makes sleep better and reduces stress. This can lead to fewer nightmares.
Studies show a link between sleep apnea and nightmares. They found that more anxiety and depression are linked to nightmares. Custom oral appliances help keep airways open.
These treatments, along with relaxation and a bedtime routine, can help. Even small changes, like avoiding late-night snacks, can help.
If you snore a lot or feel tired all the time, get a sleep study. Early treatment with CPAP or oral appliances can help. It improves sleep and lowers stress.
Good sleep health means better days and nights. Start today by talking to a specialist. Take small steps towards better sleep.