Imagine drinking something that makes you smarter, keeps you healthy, and helps you stay fit. Green tea is more than just a warm drink. It’s a centuries-old treasure full of health benefits. It comes from ancient Asia and is loved worldwide today.
Green tea has special helpers called antioxidants. These are like superheroes for your body. They fight off diseases and keep you healthy. Studies show green tea drinkers might have lower risks of heart disease and obesity.
But is all this really true? A 2020 study found green tea drinkers had a 64% lower chance of memory loss. Another study in 2022 showed four cups a day could help women lose 44% of belly fat. Could drinking green tea be a simple way to improve your health?
Let’s look at why green tea’s special mix might be good for you. It has 30% to 40% polyphenols by weight. This might make it a great addition to your daily routine.
Key Takeaways
- Green tea’s polyphenols and antioxidants may reduce risks of chronic diseases.
- Studies suggest it lowers obesity risk and improves heart health.
- It contains caffeine and L-theanine, which together boost focus without jitters.
- Up to eight cups daily is safe when consumed as a beverage.
- It’s linked to better brain function and blood sugar control.
What Makes Green Tea Special?
Green tea is special because of its history and the science behind it. It has stood the test of time for good reasons.
The Ancient Origins of Green Tea
Green tea started in China over 4,000 years ago. It was valued for its health benefits before it became a daily drink. Its popularity has grown across Asia and into the world today.
Understanding Green Tea’s Composition
Green tea is packed with green tea polyphenols, making it a superfood. It contains:
- Catechins (like EGCG) that fight oxidative stress.
- L-theanine for calm focus.
- Vitamins and minerals like vitamin C and potassium.
These ingredients help with heart health and mental clarity.
Types of Green Tea Available in the US Market
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_zeWne-mLcc
| Type | Origin | Taste |
|---|---|---|
| Matcha | Japan | Earthy, vibrant |
| Dragon Well (Longjing) | China | Grassy, nutty |
| Sencha | Japan | Light, vegetal |
| Jade Oolong | Taiwan | Floral, sweet |
Each type has its own green tea antioxidants. Trying different ones can help you find your favorite.
The Science-Backed Green Tea Benefits for Your Body
Green tea is more than just a drink. It’s full of compounds that help your body. EGCG is a key antioxidant. It fights oxidative stress and reduces inflammation, which can prevent chronic diseases.

Green tea helps with weight management too. Studies show it can help you lose up to 2.6 pounds. It also helps shrink your waist by 1.9 cm. This is thanks to its caffeine and EGCG, which boost fat burning.
- EGCG reduces inflammation linked to heart disease and diabetes.
- Green tea caffeine content provides steady energy without jittery crashes.
- Antioxidants may slow age-related brain decline by protecting nerve cells.
| Benefit | Key Fact |
|---|---|
| EGCG effects | Blocks free radicals that damage DNA and cells |
| Weight management | Study shows 2.6 lb average weight loss with daily intake |
| Caffeine levels | About 35 mg per cup—less than coffee but enough to boost alertness |
Green tea also lowers LDL cholesterol and improves insulin sensitivity. Japanese research found drinking 3+ cups daily lowers stroke risk by 20%. Drinking green tea gives your body antioxidants, caffeine, and EGCG. These work together for long-term health.
How Green Tea Boosts Your Immune System
Your body needs balance to stay healthy. Green tea’s natural compounds help your immune system. They fight germs and reduce inflammation.
Antioxidant Properties That Fight Inflammation
Green tea’s anti-inflammatory effects come from antioxidants like EGCG. These molecules:
- Neutralize free radicals that damage cells
- Block enzymes linked to chronic inflammation
- Reduce TNF-α and IFNγ, proteins that fuel inflammation

Green Tea’s Role in Cold and Flu Prevention
Studies show green tea compounds like catechins disrupt viruses. A 2020 test-tube study found EGCG blocks flu virus replication. Healthcare workers who drank catechin-rich beverages cut upper respiratory infections by 50% in 12 weeks. These antioxidants:
- Bind to virus surfaces to stop cell entry
- Boost IgM and IgG antibodies that target pathogens
Supporting Your Body’s Natural Defenses
Green tea doesn’t just “boost” immunity—it balances it. Key points:
- EGCG increases CD4+ T cells for targeted immune responses
- Enhances Th1/Th2 balance to avoid overactivity
- Promotes B-cell activity for long-term immune memory
By modulating genes like IL-1β and IgM, green tea helps your body stay ready without overreacting. Small steps like sipping this brew daily can make a big difference.
Green Tea and Heart Health: What You Need to Know
Green tea is good for your heart, and science backs it up. Studies show that green tea’s EGCG can lower bad LDL cholesterol. It also raises good HDL levels. A 2018 study in the Journal of the American Heart Association found it slows down HDL decline and lowers LDL.

- Cholesterol Control: Green tea’s catechins stop harmful protein plaques. This reduces artery blockage risks.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Drinking it regularly may lower blood pressure in people with hypertension. But, effects can vary.
- Endothelial Support: EGCG boosts nitric oxide production. This improves blood vessel flexibility and circulation.
Lab research shows EGCG breaks down dangerous blood vessel plaques. But, human studies are still ongoing.
Studies, like a 2013 review, show drinking two+ cups daily can lower CVD mortality by 22-33%. But, remember: green tea and heart health benefits are best when it’s unsweetened. Don’t add sugar, as it can reduce antioxidants. Enjoy it with a balanced diet to get the most heart-protective benefits.
Can Green Tea Help with Weight Management?
Green tea has been linked to weight loss for years. It’s not a quick fix, but research shows it can help. Let’s explore how it might fit into your routine.

Metabolism-Boosting Properties
Green tea contains catechins, like EGCG, which work with caffeine. This combo can slightly increase your metabolic rate. Studies suggest it may help burn more fat when you’re not moving.
A 2023 review found green tea drinkers had lower BMI and waist measurements. This was especially true for women.
- EGCG helps break down fats, aiding weight management.
- Drinking 3-4 cups a day may raise calorie burning by 4% daily.
- No magic pill: Effects are modest but stack well with healthy habits.
Green Tea as Part of a Healthy Weight Loss Plan
For the best results, pair green tea with a balanced diet. Here are some tips:
- Drink 2-3 cups daily between meals to avoid caffeine overload.
- Choose loose-leaf varieties for higher catechin content than bottled teas.
- Aim for 1-2 mg of caffeine per pound of body weight daily (e.g., 200 mg for a 200-lb person).
Combining Green Tea with Exercise
“Exercise amplifies green tea’s fat-burning effects,” says a 2022 study linking aerobic workouts with green tea consumption to 10% higher fat oxidation.
Time your brew: Sip a cup 30 minutes before workouts to boost endurance. Pair with 150+ minutes of weekly exercise for synergy. Always stay hydrated and consult a doctor if pregnant or breastfeeding.
Mental Clarity and Focus: Green Tea’s Brain Benefits
When you sip green tea, you’re giving your brain a boost. Green tea for brain health is more than just a trend. It’s supported by science. The amino acid L-theanine in green tea pairs with caffeine for calm focus, unlike coffee’s crash.

- Improved task performance: A study in Scientific Reports found green tea drinkers had better mental task results and lower stress markers like reduced blood flow in tense areas.
- Sharper focus: L-theanine increases alpha brain waves, promoting relaxed attention. This makes green tea for mental clarity a natural choice for work or study sessions.
- Long-term protection: Regular consumption may lower the risk of cognitive decline by 64% in middle-aged adults, per a 2020 study.
Matcha, a powdered green tea, showed even stronger effects in trials. Participants who drank it daily for 12 weeks scored higher on attention tests than those who took caffeine alone. The key? L-theanine balances caffeine’s energy, easing stress while boosting alertness. Plus, green tea’s antioxidants like EGCG shield brain cells from damage, slowing oxidative stress linked to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Next time you need to tackle a tough project, reach for green tea. Its unique blend of L-theanine and natural caffeine could be your new productivity ally—without the crash.
How to Incorporate Green Tea into Your Daily Routine
Starting a green tea daily routine is easy. It’s great for both newbies and those who want to try more. Here’s how to make it a part of your daily life.
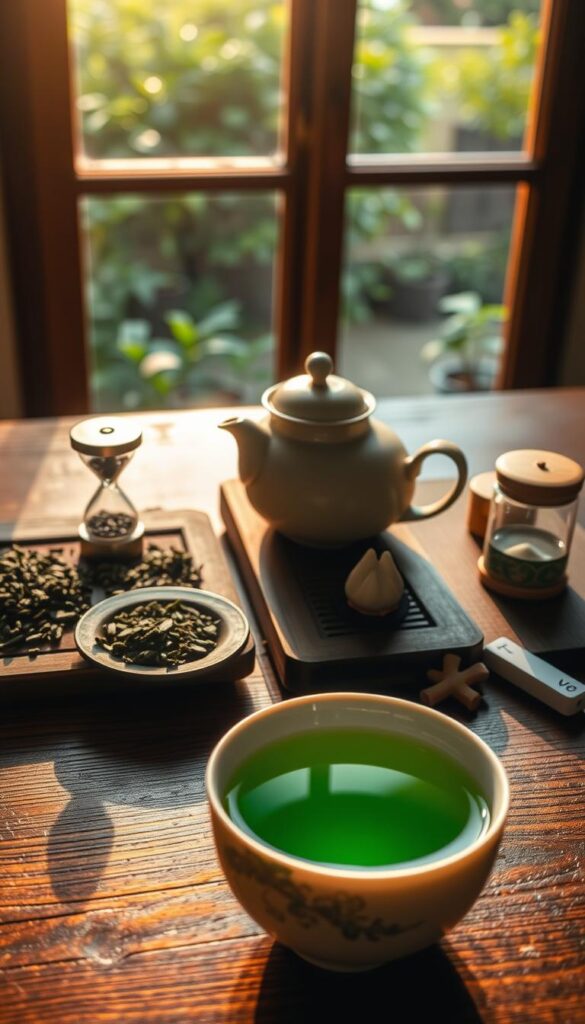

- Heat water to 175–185°F (80–85°C) – never boil it, as high heat can make tea bitter.
- Steep for 1–3 minutes. Oversteeping reduces antioxidants and adds harshness.
- Use loose-leaf tea for richer flavor or choose trusted brands like 6:00 PM Tea for quality.
Best Time to Drink Green Tea:
Drink your first cup in the morning for a caffeine kick (1–2 cups daily). Don’t drink it close to bedtime to avoid sleep issues. For a mid-day pick-me-up, enjoy it with a snack. After working out? Try Bright Eyed blends to help with recovery.
Get creative beyond the cup:
- Swap water for brewed green tea in oatmeal or smoothies.
- Marinate tofu in green tea, soy sauce, and ginger for a savory dish.
- Mix cooled tea into salad dressings or popsicles for a refreshing twist.
Making green tea a habit is easy when you mix practicality with fun. Adjust brewing methods, pick the right moments to drink it, and experiment with recipes to keep your routine fresh.
Potential Side Effects and Who Should Exercise Caution
Green tea is safe for most adults when drunk in small amounts. It’s key to know about green tea side effects and who should drink less. Here’s what to think about before making your next cup:
- Caffeine sensitivity: Too much caffeine can cause jitters, insomnia, or a fast heart rate. Matcha and gyokuro have more caffeine, so be careful if you’re sensitive.
- Digestive discomfort: Tannins might upset your stomach, cause nausea, or acid reflux, especially if you drink it on an empty stomach.
- Iron absorption: Tannins can lower iron from plant foods by up to 25%. Drinking tea with vitamin C can help with iron absorption.
- Medication interactions: Green tea can interact with blood thinners, statins, and ADHD medications.

Those taking green tea extract supplements should be careful. High doses can harm the liver in rare cases. The quality of supplements varies since the FDA doesn’t check herbal products. Choose brands that have third-party testing.
Pregnant or nursing women should drink no more than 16 oz of green tea a day. This is to avoid caffeine risks. People with heart issues, anxiety, or iron deficiencies should talk to a doctor before drinking more.
- Stick to 2-3 cups daily (200-300 mg caffeine total)
- Avoid drinking tea with meals to protect iron absorption
- Opt for decaf versions if sensitive to caffeine
Pay attention to how your body reacts. Stop drinking tea if you get headaches, irregular heartbeats, or stomach pain. If unsure, talk to a doctor before adding supplements.
Conclusion: Making Green Tea a Healthy Part of Your Lifestyle
Green tea is more than just a drink. It has antioxidants like EGCG that help your heart, brain, and weight. Enjoying it mindfully can make it a key part of your health routine.
Start with 1-2 cups a day. If you can, drink 3-5 cups. Choose loose-leaf tea for the best health benefits.
For weight loss, drink green tea with healthy food and exercise. The catechins in green tea can help burn fat. But, it’s all about your lifestyle.
Drink unsweetened tea to avoid sugar. If caffeine bothers you, try decaf or drink it after noon.
Studies show green tea can lower cancer risks and improve bones. But, if you have iron issues, drink it between meals. Always talk to a doctor if you’re on blood thinners or have a sensitive stomach.
Try matcha, sencha, or genmaicha to find your favorite. Mix it into smoothies or iced drinks. Remember, it’s the little changes that count.
Small steps like drinking green tea instead of soda can make a big difference. Enjoy the journey to better health, one cup at a time.
FAQ
What are the main health benefits of drinking green tea?
Drinking green tea can help your heart, aid in weight loss, and boost brain function. It also strengthens your immune system. The antioxidants, especially EGCG, are key to its health benefits.
How does green tea compare to other types of tea?
Green tea is special because it’s minimally processed. This keeps its antioxidants and health benefits intact. Unlike black and oolong tea, green tea is less oxidized, which preserves its health-promoting properties.
How much green tea should I drink daily to experience its benefits?
For the best health benefits, drink 3-5 cups of green tea each day. This amount lets you enjoy its health benefits while staying balanced.
Are there any side effects associated with drinking green tea?
Green tea is usually safe, but some might feel caffeine’s effects. This can cause anxiety or upset stomach. If you have health concerns, talk to a doctor first.
Can drinking green tea help with weight loss?
Yes, green tea can aid in weight loss. It boosts metabolism and fat burning when you eat well and exercise. But, it’s not a quick fix and should be part of a bigger plan.
What is the best time to drink green tea for maximum benefits?
Drinking green tea in the morning is great for energy and focus. Having it mid-afternoon can help you stay productive. Drinking it before meals may also help with digestion and metabolism.
How do the types of green tea differ in terms of taste and health benefits?
Green teas like sencha, matcha, and Dragon Well have different tastes and health perks. Matcha is powdered and packed with antioxidants. Sencha has a fresh, grassy taste. Trying different types can make your green tea experience better.
Does bottled green tea provide the same benefits as freshly brewed?
Usually, bottled green tea has fewer antioxidants and more sugar than fresh-brewed. Freshly brewed tea or unsweetened bottled tea is better for your health.
How can I incorporate green tea into my cooking?
You can use green tea in cooking by making it a liquid for rice or oatmeal. Add it to smoothies or make matcha-infused baked goods. These ideas let you enjoy green tea’s flavors and benefits in tasty dishes.