Omega-3 benefits include better brain function and less joint pain. But many overlook this nutrient. This guide shows how to get enough omega-3 from food like salmon or barramundi. It also explains why supplements might be needed. Learn how balancing your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio can improve your energy, focus, and health.
- Omegaga-3s support brain function, heart health, and reduce inflammation.
- Most americans have an unbalanced omega-6 to omega-3 ratio (20:1 vs. the recommended 4:1).
- fish like salmon and barramundi provide over 650 mg of omega-3s per serving.
- EPA and DHA from fish are more bioavailable than plant-based ALA sources.
- addinging omega-3 rich foods or supplements can boost cognitive performance and mood.
What Are Omega 3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids. They are polyunsaturated fats your body needs but can’t make. These nutrients are key for cell health and brain function. They also help your heart work well.
The Three Main Types of Omega-3s
There are three main types of omega-3 you should know:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): Found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, EPA supports heart health and reduces inflammation.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): Abundant in fish and algae, DHA is a building block for brain and eye health.
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): Plant-based sources like flaxseeds and walnuts provide ALA, which the body can convert into EPA and DHA—but only in small amounts.
Why Your Body Can’t Produce Enough Omega-3
Your body can’t make EPA DHA ALA well. It tries to turn ALA from plants into EPA and DHA, but it’s slow. For most people, eating foods or taking supplements is the best way to get enough.
The Science Behind These Essential Fats
Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fats with a special structure. This structure lets them make cell membranes flexible and act as signals. But, our diets often have too many omega-6 fats. This can cause chronic inflammation and health problems.
Heart Health Benefits of Omega 3
Omega 3 fats have been studied for decades. They are key for heart health. They help with high triglycerides and inflammation.
Research shows omega 3s can lower heart disease risk. They also improve artery function.
- Lower triglycerides: Reduces harmful blood fats linked to heart strain.
- Stabilize heart rhythm: Lessens the chance of dangerous arrhythmias.
- Reduce plaque buildup: Slows the hardening of arteries that can lead to blockages.
- Lower blood pressure: Helps arteries stay flexible and responsive.
“The VITAL trial found a 28% drop in heart attack risk for those taking fish oil, especially in people who rarely ate fish.”
High-quality fish oil heart health supplements are very effective. The REDUCE-IT trial showed a 25% reduction in heart events. Even 1,000 mg of EPA/DHA daily can help.
Doctors suggest this amount for heart condition management. It’s a small step towards better heart health.
While fish oil is beneficial, choose trusted brands to avoid contamination. Combine supplements with exercise and a healthy diet. Simple choices can greatly improve heart health over time.
Omega 3 for Brain Function and Mental Health
Your brain needs omega-3s to work right. DHA, a key omega-3, makes up 40% of the brain’s fatty acids. It’s vital for brain development from birth to adulthood.
Early life exposure to DHA-rich diets helps create neural pathways. These are key for learning and memory. For kids, getting enough DHA during pregnancy and early years boosts cognitive skills later.

Supporting Cognitive Development
Research shows 900 mg of DHA daily helps older adults remember better. It also boosts brain blood flow during tasks. Kids with ADHD often have low omega-3 levels.
Trials with 510 mg DHA supplements reduced hyperactivity and improved focus in kids. For Alzheimer’s, omega-3s may slow decline by protecting neurons from damage.
Managing Depression and Anxiety
Omega-3s help mood by reducing brain inflammation and balancing neurotransmitters like serotonin. A 2012 study found 2 g of fish oil increased brain activity tied to cognitive benefits.
Combining fish oil with antidepressants can improve results, especially with higher EPA doses. Even small daily intake (300 mg) improved attention in people with low DHA levels.
Potential Benefits for ADHD and Alzheimer’s
- ADHD: Fortified foods with 510 mg DHA and 100 mg EPA cut symptom severity by 25% in children
- Alzheimer’s: 2.2 g of omega-3 improved memory in older adults, with some trials showing 26% better executive function
- Children with reading deficits saw behavior improvements after 600 mg DHA supplements
More research is needed, but these findings show omega-3s’ role in mental health. Getting enough DHA and EPA through diet or supplements supports omega 3 brain health at all ages.
How Omega 3 Fights Inflammation in Your Body
Omega 3’s anti-inflammatory effects start at a cellular level. Your body turns EPA and DHA into molecules like resolvins and protectins. These molecules block pro-inflammatory signals.
This helps reduce omega 3 inflammation linked to conditions like arthritis and heart disease.
Reducing Chronic Inflammation
- EPA and DHA replace arachidonic acid in cell membranes, cutting production of harmful eicosanoids.
- Resolvin E1 and D1 from omega 3s slow neutrophil activity and curb cytokines like TNF-α.
- Studies show 1.3g daily of EPA+DHA maximizes anti-inflammatory eicosanoid production.
| Molecule | Source | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Resolvin E1 | EPA | Inhibits neutrophil migration |
| Resolvin D1 | DHA | Promotes inflammation resolution |
| Protectin D1 | DHA | Reduces TNF-α and IL-1β |
Supporting Joint Health and Arthritis Relief
For joint health, omega 3s lower pain and stiffness in omega 3 arthritis cases. A study found fish oil raised anti-inflammatory molecules for up to 24 hours. Key takeaways:
- Supplements reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and CRP in rheumatoid arthritis.
- EPA/DHA inhibit COX-2 enzymes, mimicking NSAIDs but without stomach risks.
Your diet’s omega-6/omega-3 ratio matters. The typical 20:1 ratio in American diets fuels inflammation. Aim for 4:1 or lower by adding fatty fish or supplements.
Top Food Sources Rich in Omega 3
Boost your omega 3 intake with these nutrient-packed omega 3 foods. From the sea to your pantry, here’s how to pick the best fatty fish sources and plant-based options for daily health.
“Even small portions of omega 3-rich foods can make a big difference in heart and brain health.” — Dr. Frank Sacs, Harvard School of Public Health
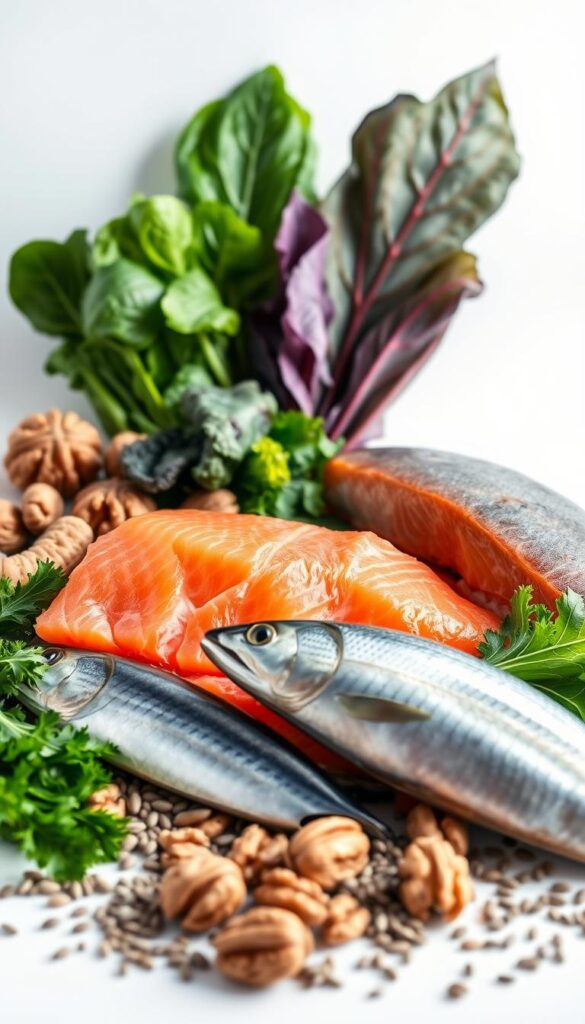

Fatty fish are the top fatty fish sources. Mackerel has 4,580 mg of EPA/DHA per 3.5 oz serving. Salmon and herring follow with 2,150 mg each. Wild salmon has 1.22g DHA, while farmed has 1.24g.
Sardines and oysters also offer omega 3s. Sardines have 1,463 mg EPA/DHA per cup. Oysters have 0.23g DHA and 0.30g EPA. Eat 2-3 servings a week for heart health.
For plant-based eaters, ALA food sources like flaxseeds and chia seeds are great. They have 5g ALA per oz. Walnuts and hemp seeds also have 2.5g and 2.6g ALA per ounce, respectively.
Even edamame has 0.28g ALA per half-cup. Though ALA converts poorly to DHA/EPA, these foods are rich in fiber and antioxidants.
Pair fatty fish with greens or whole grains for balanced meals. Sprinkle chia on oatmeal or blend flax into baked goods. Choose fresh or canned options for simplicity. Your body will thank you for these smart swaps!
Supplementing With Omega 3: What You Need to Know
Choosing the right omega 3 supplements can feel overwhelming. But knowing the facts makes it simpler. Start by understanding the options and what to look for.
Fish Oil vs. Krill Oil vs. Algal Oil
Each type of omega 3 supplements has its own benefits:
- Fish Oil: The most studied option. Look for fish oil quality certifications like IFOS or MSC. It has high EPA/DHA but may taste fishy if low quality.
- Krill Oil: Contains astaxanthin, an antioxidant, and phospholipids for better absorption. Krill oil benefits include better bioavailability but may cost more.
- Algal Oil: A vegan-friendly choice rich in DHA. Sustainable and free of contaminants, ideal for plant-based diets.

| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Fish Oil | High EPA/DHA content | Potential contaminants without proper certification |
| Krill Oil | Includes antioxidants and phospholipids | Higher cost and sustainability debates |
| Algal Oil | Plant-based, sustainable | Lower EPA compared to fish oil |
Finding the Right Omega 3 Dosage
Start with 250–500mg EPA/DHA daily for maintenance. For heart health or inflammation, aim for 1000–3000mg. Always check labels for actual EPA/DHA amounts—not total oil content.
What to Look for on Supplement Labels
Prioritize supplements with fish oil quality seals like USP or NSF. Avoid ethyl esters; choose triglyceride forms for better absorption. Enteric coating reduces fishy aftertaste. Store in a cool, dark place to prevent rancidity.
Consult a healthcare provider before use, especially if on blood thinners or other medications. Omega 3 supplements are safest when paired with a balanced diet.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Most people find omega-3 supplements safe. But knowing about omega 3 side effects and fish oil interactions is key. You might feel a bit sick, have bad breath, or burp.
But, serious problems are rare. They include bleeding more, especially if you take blood thinners. This is because fish oil interactions with these drugs can increase the risk.

- Common omega 3 side effects: Belching, diarrhea, nausea
- Medication concerns: Anticoagulants, diabetes drugs, immunosuppressants
- Special care groups: Pregnant individuals, allergy sufferers, surgical patients
| Drug Type | Potential Interaction | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Blood thinners | Increased bleeding risk | Jalili et al. (2007) |
| Diabetes medications | Altered blood sugar | Kasim et al. (2018) |
| Immunosuppressants | Reduced efficacy | Jørgensen et al. (2021) |
Choose supplement precautions like reputable brands to avoid heavy metal contamination. Always check omega 3 safety with your doctor before use, especially if on medications or managing chronic conditions. Start with small doses and store capsules properly to prevent oxidation.
Prioritize quality: look for third-party tested products and follow dosage guidelines for optimal omega 3 safety.
Creative Ways to Add More Omega 3 to Your Diet
Boosting your omega-3 intake is easy. Just make a few simple swaps and plan your meals wisely. Try these omega 3 recipes and omega 3 diet tips to make healthy eating simple.
Omega 3-Boosted Recipes
Get creative with these easy ideas:
- Mix ground flaxseed or chia into oatmeal, yogurt, or pancake batter for a omega 3 recipes boost.
- Make sardine pâté with lemon and herbs—increase omega 3 intake by serving with whole-grain crackers.
- Top salads with walnuts and a dressing made from canola oil and Dijon mustard.
- Bake salmon or mackerel with roasted veggies for a quick dinner packed with DHA and EPA.
- Blend spirulina into smoothies or sprinkle nori flakes on soups for a seaweed boost.

“Pairing fish with flavorful sauces keeps meals exciting,” says Josh Goldman, who enjoys sardines with tangy horseradish. “Variety in preparation matters.”
Meal Planning for Optimal Intake
Plan meals to hit your omega-3 goals consistently:
- Choose fatty fish twice weekly: Try salmon burgers on Monday, grilled mackerel on Thursday.
- Stock your pantry with canned sardines, frozen barramundi fillets, and prepackaged chia seeds.
- Prep chia pudding on Sunday for grab-and-go breakfasts all week.
- Swap out peanut butter for walnut butter in sandwiches or smoothies.
Pairing omega 3 meal planning with pantry staples like ground flaxseed ensures you never fall short. Even small additions—like hemp seeds on yogurt or flax in muffins—add up. Experiment with texture and flavors to keep your diet fresh and nourishing.
Conclusion: Making Omega 3a Cornerstone of Your Wellness Routine
Creating an omega 3 wellness plan is easy. Start with small changes to your daily omega 3 routine. Eat foods like salmon, walnuts, and chia seeds. These foods give your body the fats it needs for brain, heart, and joint health.
Most people don’t get enough omega 3s. But, making these changes can bring big health benefits. It’s more than just eating right.
Choose good sources of omega 3s. Fatty fish has EPA and DHA, while flaxseeds have ALA. If you can’t get enough from food, try supplements like Naturesage’s Clary Sage Seed Oil. It’s clean and safe.
Make sure to pick supplements that have been tested. Use an Omega-3 Index test to see if you’re getting enough. Aim for levels above 8% for best health.
Living an omega 3 lifestyle means being consistent. Try new recipes with salmon, add chia seeds to smoothies, or remember to take your supplement. Even small changes help a lot.
By doing these things, you help your body fight off sickness and stay sharp. You’re making a smart choice for your future health. And it won’t make your life less tasty or convenient.
FAQ
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are fats our bodies can’t make. They’re key for heart, brain, and joint health. You can find them in fish, plant oils, and nuts and seeds.
What are the main types of omega-3s?
There are three main omega-3s: EPA, DHA, and ALA. EPA and DHA are in fish. ALA is in plants like flaxseeds and walnuts.
Can I get enough omega-3 through diet alone?
Getting enough omega-3 through food is possible but hard for many. Eating omega-3-rich foods or taking supplements can help.
How do omega-3s support heart health?
Omega-3s help the heart by lowering triglycerides and blood pressure. They also reduce heart inflammation. Studies show they lower heart disease risk.
Are omega-3s beneficial for brain health?
Yes! Omega-3s, especially DHA, are vital for brain health. They improve mood, memory, and thinking. They help with depression and ADHD too.
How can omega-3s help with inflammation?
Omega-3s fight inflammation in the body. This is good for people with chronic conditions like arthritis.
What are the best food sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
Best sources are cold-water fish like salmon and mackerel. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are good plant options. Algal oil is a vegan DHA source.
How should I choose an omega-3 supplement?
Choose supplements with third-party testing. Look at EPA and DHA content and the oil form. Avoid processed products and those with a fishy smell.
What are the potential side effects of omega-3 supplements?
Most people do fine with omega-3s, but some may get upset stomach or taste fishy. High doses can increase bleeding risk. Always talk to a doctor before starting.
Can I use recipes to increase my omega-3 intake?
Yes! Adding flaxseed to smoothies or making salmon dishes is tasty and increases omega-3 intake.
Do I need to take supplements if I consume fish regularly?
If you eat fatty fish 2-3 times a week, you might not need supplements. But if your diet lacks these foods, or if you’re vegetarian or vegan, supplements can help.