Did you know up to 44% of people snore regularly? Yet, nearly 80% of obstructive sleep apnea cases go unnoticed each year. This means millions might ignore a serious sleep issue. Knowing the difference between normal snoring and sleep apnea is key to your health.
Imagine waking up gasping for air dozens of times a night. This isn’t just loud breathing; it’s a warning sign for OSA. Simple at-home tests can spot sleep apnea with 98% accuracy. Yet, many still guess instead of testing.
Key Takeaways
- 44% of adults snore regularly, but sleep apnea stops breathing for 10+ seconds at a time.
- Untreated OSA raises risks for heart disease, diabetes, and strokes.
- Home tests cost $189 and arrive in 2-4 days—far cheaper than $3,000 lab studies.
- Daytime symptoms like headaches or fatigue may link to sleep apnea, not just snoring.
- Over 80% of OSA cases stay hidden, making self-tests vital for early detection.
Why Distinguishing Between Snoring and Sleep Apnea Matters
Snoring is common—up to 44% of people do it—but ignoring sleep apnea symptoms can have serious consequences. Sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) involve more than loud noises. During sleep, your breathing stops or slows for 10+ seconds, lowering blood oxygen levels and stressing your heart. Left untreated, this can lead to long-term health risks.
- High blood pressure and heart disease risks rise due to repeated oxygen drops.
- Daytime sleepiness caused by sleep apnea impairs focus and memory.
- Untreated OSA increases chances of type 2 diabetes and stroke.
Even children aren’t immune. Kids with undiagnosed OSA may face learning or behavioral struggles. Yet over 80% of sleep apnea cases go unrecognized. Many mistake it for regular snoring, delaying life-changing treatments like CPAP therapy or surgery. Recognizing symptoms like gasping for air, morning headaches, or persistent fatigue helps you seek timely care.
Knowing the difference protects your health. Early diagnosis through sleep studies can prevent complications and improve your quality of life. Your sleep patterns hold clues—don’t let common snoring mask a silent threat to your well-being.
Understanding the Root Causes of Snoring
Exploring snoring causes begins with sleep reactions. Air struggles to pass through airways, causing throat or nose vibrations. Simple habits or anatomical fixes can often stop this noise.
Common Anatomical Factors Behind Snoring
Your body’s shape is key. Here’s what might cause the sound:
- Large neck narrows airways
- Big tonsils or a crooked septum block airflow
- Loose throat tissues relax more at night
Lifestyle Contributions to Snoring
Daily choices can make snoring better or worse. Here’s how to fight snoring prevention:
- Extra weight adds fatty tissue around airways
- Alcohol relaxes throat muscles more
- Smoking irritates and swells airways
- Sleeping on your back traps the tongue
How Snoring Affects Your Sleep Quality
Snoring disrupts sleep cycles, even without sleep apnea. It leads to daytime tiredness. It also affects partners, with 37 million adults snoring regularly.
Improving sleep means better rest for all.
Sleep Apnea: More Than Just Loud Snoring
Snoring can mess up your sleep, but sleep apnea is much worse. It causes breathing stops that can harm your health. Knowing the types and risks helps get an early sleep apnea diagnosis.
Obstructive vs. Central Sleep Apnea: Key Differences

| Type | Cause | Common sleep apnea symptoms | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) | Collapsed throat muscles blocking airflow | Gasping, loud snoring with pauses, morning headaches | Most common type |
| Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) | Brain fails to signal breathing muscles | Shallow breaths, insomnia, shortness of breath | Rare compared to OSA |
Risk Factors for Developing Sleep Apnea
- Excess weight: 44% of obese adults face higher risk
- Neck circumference over 17 inches (men) or 16 inches (women)
- Age over 40 increases likelihood
- Family history of sleep disorders
The Hidden Health Impacts of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Untreated apnea can harm your body in ways you might not see. Sleep apnea symptoms like constant tiredness are just the beginning. If left untreated, it can lead to:
- High blood pressure and heart disease
- Increased risk of stroke and diabetes
- Cognitive decline and mood swings
Getting an early sleep apnea diagnosis can stop these problems. See a doctor if you snore loudly, gasp, or feel tired all day.
Take Our Snoring vs Sleep Apnea Self-Test
Wondering if your snoring could signal sleep apnea? Use this snoring vs sleep apnea self-test to assess your risk. It’s not a full test, but it can guide you. Start by answering these questions:
“Symptoms like gasping for air or chronic fatigue shouldn’t be ignored—early action can improve long-term health outcomes.”
Ask yourself:
- Does your snoring wake others or disrupt sleep?
- Have you noticed pauses in breathing during sleep?
- Do you feel unrested even after 7+ hours of sleep?
- Do you experience morning headaches or dry mouth regularly?

Scoring your risk: Yes answers to 2+ questions suggest discussing sleep apnea testing with a doctor. The snoring vs sleep apnea self-test also highlights red flags like unexplained high blood pressure or frequent concentration issues.
| Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) | Severity |
|---|---|
| 0–5 events/hour | Normal |
| 5–15 events/hour | Mild apnea |
| 15–30 events/hour | Moderate apnea |
| >30 events/hour | Severe apnea |
Professional sleep apnea testing confirms results. Home tests cost $100–$500 and measure breathing patterns, while in-lab studies provide detailed data. If your self-test score raises concerns, act fast. Your health depends on it.
Treatment Options for Better Sleep
Choosing the right snoring treatment or sleep apnea management plan starts with understanding your symptoms. Many options exist, from simple fixes to medical devices. Talk to a doctor to tailor solutions to your needs.
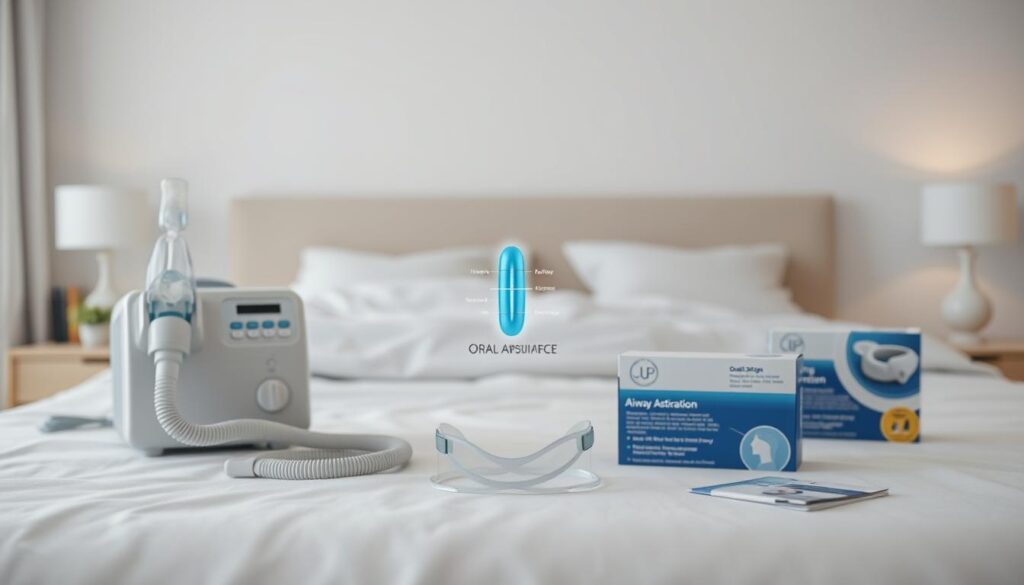

Simple Remedies for Occasional Snoring
Try these snoring remedies for mild cases:
- Nasal strips to open airways
- Custom-fitted mouthpieces prescribed by dentists
- Throat exercises like tongue and palate stretches
- Side-sleeping pillows to avoid backlying
CPAP and Other Sleep Apnea Interventions
For sleep apnea management, CPAP therapy is a top choice. Machines send pressurized air to keep airways open, effective for 70-90% of users. Other options include:
- Oral appliances to reposition the jaw
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) surgery for severe cases
- Positional therapy devices to prevent back-sleeping
Lifestyle Changes That Improve Both Conditions
| Change | Snoring Benefits | Sleep Apnea Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Weight loss | Reduces throat tissue vibration | Cuts apnea episodes by 30-50% |
| Avoiding alcohol | Prevents muscle over-relaxation | Reduces airway collapse risks |
| Quit smoking | Decreases throat inflammation | Improves lung function |
Making these changes can boost results from medical treatments. Pair them with professional care for best outcomes.
When to Consult a Sleep Specialist
If you often gasp or pause in breathing while sleeping, it’s time to get help. Sleep apnea diagnosis can tell if you have a serious issue that needs medical attention.
- Regular snoring paired with choking sensations
- Witnessed breathing pauses during sleep
- Daytime sleepiness despite 7+ hours of sleep
- Unexplained morning headaches
- High blood pressure linked to sleep issues

“Up to 44% of people snore regularly, but not all need treatment. Persistent symptoms warrant professional evaluation.”
Sleep apnea testing can be done with overnight studies or at-home devices. A clinic-based sleep apnea diagnosis uses polysomnography to track brain waves and breathing. Home tests check heart rate and blood oxygen to see how bad it is. Both help doctors find the best treatment.
If your doctor thinks you might have sleep apnea, they might send you for a sleep study. These tests show if you stop breathing 5+ times an hour. This is a sign of obstructive sleep apnea. Early sleep apnea testing can stop heart problems or diabetes from getting worse.
Don’t wait if symptoms are affecting your daily life. A specialist can help you find the best way to get better sleep. They’ll make sure you’re safe and get the care you need.
Conclusion: Your Path to Restful Sleep
Your sleep health is very important. If you think you might be snoring or have sleep apnea, act fast. Over 25% of adults have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which is treatable.
Small changes like staying at a healthy weight or avoiding alcohol before bed can help. These steps are crucial for snoring prevention.
If you think you might have OSA, talk to a doctor. They can suggest lifestyle changes or use devices like CPAP machines. Home sleep tests (HST) are easy and cheap, but in-lab studies (PSG) give more details.
Even if tests show you’re fine, you can still improve your sleep. Tips like sleeping on your side or quitting smoking can help.
Don’t be shy about getting help. Sleep studies use cool tools like EEGs and pulse oximeters. They track your brain and breathing, giving accurate results.
While you might feel a bit uncomfortable, the benefits are worth it. Good sleep means more energy and focus tomorrow.
Start your journey to better sleep now. Whether it’s simple changes or medical advice, acting early is key. Try snoring prevention tips or schedule a check-up. Your future of restful sleep starts today.